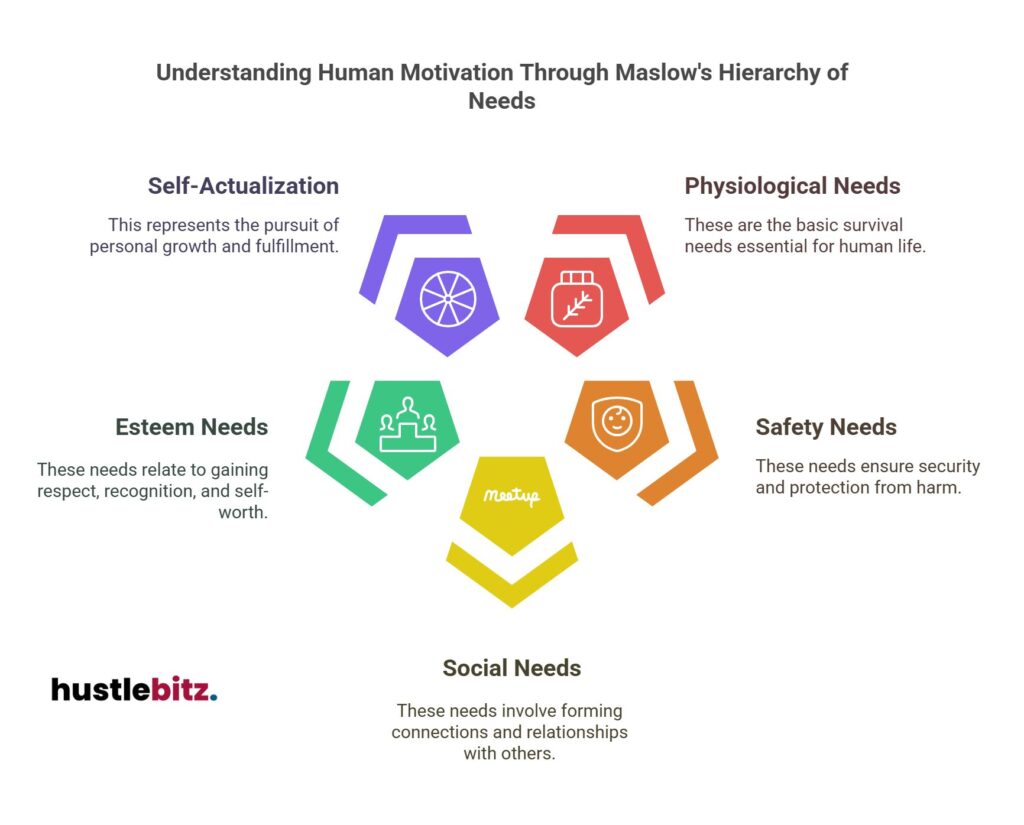
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs presents a structured approach to understanding human motivation, emphasizing the progression through five levels: physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization. Each level represents critical needs that must be met for individuals to advance to higher motivations. For instance, fulfilling basic physiological needs establishes a foundation for safety and emotional security. As individuals navigate these needs, they develop relationships and self-esteem, ultimately striving for personal growth and fulfillment. This framework not only enhances personal development but also informs strategies for motivation within organizational settings. Exploring these concepts further can provide deeper insights.
Key Takeaways
- Maslow’s Hierarchy defines five levels of needs, guiding human motivation from basic survival to self-actualization.
- Meeting physiological and safety needs is essential for fostering motivation toward higher-level emotional and social fulfillment.
- Social connections and interpersonal relationships play a crucial role in enhancing emotional support and overall well-being.
- Esteem needs drive individuals to seek recognition and validation, impacting self-worth and motivation.
- Self-actualization represents the ultimate goal, promoting personal growth, creativity, and alignment with one’s true values.
Overview of Maslow’s Theory
Maslow’s Theory, widely recognized in psychology and organizational behavior, outlines a hierarchical structure of human needs that motivates individual behavior and personal development. This framework is foundational in understanding how various levels of needs influence psychological well-being and human behavior. At its core, Maslow’s motivation emphasizes the importance of fulfilling basic needs before individuals can pursue higher-level aspirations, ultimately leading to personal growth.
The theory posits that intrinsic motivation plays a crucial role in driving individuals towards self-actualization. As people progress through the hierarchy, they develop emotional intelligence and social dynamics that enhance their interactions and relationships. This progression underscores the role of cognitive needs, which include mental stimulation and creativity, vital for fostering an engaged and motivated individual.
In the context of developmental psychology, Maslow’s Theory serves as a guide for creating effective motivational strategies. It highlights how understanding the varied and evolving needs of individuals can lead to improved outcomes in both personal and professional settings.
For instance, addressing lower-level needs such as safety and belonging can create a strong foundation for higher-level pursuits, including esteem and self-actualization.
The Five Levels of Needs

Understanding the hierarchy of needs is pivotal for recognizing the five distinct levels that shape human motivation and development.
At the base lies physiological needs, which encompass biological imperatives necessary for basic survival, such as food, water, and shelter. Once these fundamental requirements are satisfied, individuals can progress to the next level, focusing on safety and security, which addresses psychological drives related to stability and protection.
The third level introduces social needs, emphasizing emotional fulfillment through relationships and belongingness. This stage highlights the importance of social dynamics, where connections with others meet the intrinsic motivation for companionship and support.
Following social needs, esteem needs emerge, which encompass both self-esteem and the desire for external validation. This level reflects individual priorities concerning recognition, accomplishment, and the respect of others.
Finally, the pinnacle of Maslow’s hierarchy is self-actualization, where individuals strive for personal growth and the realization of their full potential. This stage is influenced by cultural factors and encourages individuals to pursue their passions and aspirations, transcending societal expectations.
Each of these levels represents a vital component of human experience, guiding individuals through various developmental stages. Understanding these interconnected needs allows for a deeper insight into what drives behavior and how fulfillment at each level can influence overall motivation and well-being, ultimately shaping a more profound understanding of human psychology.
Physiological Needs Explained
Physiological needs form the foundational level of human motivation, encompassing essential requirements such as food, water, shelter, and sleep that are critical for survival. These needs are paramount as they directly influence our body functions and overall health. When physiological hunger is not adequately addressed, the survival instincts kick in, leading to various physical and psychological challenges.
To better understand the significance of physiological needs, consider the following key components:
- Nutrition Balance: A well-rounded diet is vital for maintaining energy levels and supporting bodily functions.
- Sleep Importance: Adequate sleep is crucial for recovery and cognitive function, influencing our capacity to manage stress effectively.
- Environmental Comfort: A stable living environment provides both emotional and physical reassurance, impacting our ability to thrive.
- Physical Activity: Regular movement promotes health and helps in the regulation of body functions, enhancing well-being.
- Health Requirements: Meeting basic health needs through proper hygiene and medical care is essential for preventing illness and maintaining a high quality of life.
Safety Needs in Daily Life

Safety needs encompass the fundamental requirements for security and protection, which are essential for individuals to feel stable and free from harm in their daily lives. These needs manifest in various forms, including emotional safety, financial security, and the creation of safe environments. In both personal and professional contexts, implementing effective safety protocols is critical to ensuring a sense of well-being.
Emotional safety involves establishing personal boundaries that allow individuals to express themselves without fear of judgment or harm. This aspect is vital for mental well-being, fostering a supportive atmosphere where individuals feel valued and secure.
Financial security, on the other hand, enables individuals to manage their resources effectively, reducing anxiety associated with economic instability.
Moreover, community safety plays a significant role in enhancing overall security. Engaging in crisis preparedness initiatives helps communities develop robust responses to potential threats, whether natural disasters or public safety concerns.
In workplace settings, prioritizing workplace safety through regular training and adherence to health precautions is essential not only for compliance but also for cultivating a culture of care and concern for employee welfare.
Ultimately, addressing safety needs is foundational to human motivation and productivity. By creating environments that prioritize safety—both physically and emotionally—individuals can thrive, thus allowing them to pursue higher-level needs in Maslow’s hierarchy.
This holistic approach to safety not only enhances individual well-being but also strengthens the fabric of our communities.
Social Needs and Relationships

Social needs encompass the essential human desire for connection, belonging, and interpersonal relationships, which play a crucial role in overall emotional well-being and motivation. These needs are fundamental to our social identity and influence various aspects of our lives, including personal fulfillment and professional success. Establishing strong social connections can foster a sense of community engagement, providing individuals with the emotional support necessary to navigate life’s challenges.
Key components of social needs include:
- Interpersonal relationships: The bonds we form with others create a network of support and enhance our collaborative efforts.
- Friendship dynamics: Healthy friendships contribute to our emotional well-being and can serve as a buffer against stress.
- Team collaboration: Working effectively within groups can improve productivity and foster a sense of belonging.
- Communication skills: Strong communication is essential for relationship building and conflict resolution, aiding in the maintenance of positive social interactions.
- Emotional support: Receiving and providing emotional support is critical for resilience and overall mental health.
Understanding the intricacies of these social needs is vital for personal development and organizational success. By prioritizing relationship building and effective communication, individuals can cultivate a supportive environment that not only enhances personal motivation but also encourages collective growth.
Ultimately, social needs are not merely an adjunct to our existence; they are a core component of our humanity that drives us toward greater fulfillment and connection.
Esteem Needs and Self-Worth

Esteem needs, encompassing the desire for respect, recognition, and a sense of accomplishment, are crucial for fostering self-worth and motivating individuals to achieve their full potential. These needs play a pivotal role in esteem development, where individuals engage in self-worth assessments to evaluate their personal achievements and capabilities. Confidence building is essential in this process, as it allows individuals to confront external influences that may undermine their self-esteem.
Recognition strategies, such as acknowledging achievements and providing constructive feedback, can significantly enhance self-esteem improvement. Moreover, individuals can explore validation sources, which can range from peers to personal reflections, to bolster their sense of self. Positive affirmations can serve as powerful tools in this regard, reinforcing a healthy self-identity exploration.
To illustrate the components of esteem needs, consider the following table:
| Aspect | Description |
| Confidence Building | Techniques to enhance self-belief and capability. |
| Recognition Strategies | Methods to acknowledge and celebrate achievements. |
| Validation Sources | Relationships and feedback mechanisms that reinforce worth. |
Self-Actualization: The Ultimate Goal

Self-actualization represents the culmination of personal development, where individuals strive to realize their fullest potential and pursue personal growth beyond mere self-esteem and recognition. This stage of Maslow’s Hierarchy is characterized by a deep understanding of one’s authentic self and the pursuit of life purpose. Individuals who reach this level often engage in transformative experiences that foster self-discovery and intrinsic motivation.
In the journey toward self-actualization, several key factors contribute to achieving this ultimate goal:
- Creative Expression: Engaging in artistic or innovative activities that allow for self-expression.
- Peak Experiences: Moments of intense joy and fulfillment that provide profound insights into one’s existence.
- Existential Fulfillment: A sense of meaning and purpose that transcends the individual and connects to the larger human experience.
- Individual Potential: Recognizing and harnessing one’s unique abilities and talents to make a positive impact.
- Authentic Self: Living in alignment with one’s true values and beliefs, free from societal pressures.
Through self-actualization, individuals not only find their life purpose but also contribute to the well-being of others. This process fosters a deeper connection with the world and promotes a sense of belonging.
Ultimately, self-actualization embodies the journey of becoming the best version of oneself, where intrinsic motivation fuels continuous growth and development, leading to a fulfilling and meaningful life.
Impact on Personal Development

The journey through Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs profoundly influences personal development by providing a structured framework for individuals to understand and fulfill their intrinsic motivations and aspirations. This model encourages personal growth as individuals progress through various levels, from basic physiological needs to the pursuit of self-actualization. By identifying their current position within the hierarchy, individuals can implement effective motivation strategies tailored to their specific needs.
Self-awareness practices are integral to navigating this journey. By fostering emotional intelligence, individuals can better recognize their feelings, desires, and potential barriers to growth. This heightened awareness promotes resilience building, allowing individuals to adapt more effectively to challenges encountered along their developmental path.
Goal setting becomes a vital component as individuals strive to meet their needs and aspirations. By establishing clear, achievable goals, they can maintain a sense of direction and purpose. Moreover, achieving a life balance is essential; it helps individuals allocate time and resources effectively, ensuring that their various needs are met without sacrificing overall well-being.
Incorporating mindfulness techniques into daily routines can enhance focus and clarity, reinforcing confidence boosting and continuous learning. These practices not only empower individuals to engage deeply with their goals but also cultivate a growth-oriented mindset.
Ultimately, by leveraging Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, individuals can embark on a transformative journey that aligns their motivations with their aspirations, facilitating profound personal development.
Applications in the Workplace

Applying Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in the workplace can significantly enhance employee motivation and satisfaction by addressing their fundamental needs in a structured manner.
Understanding that employee engagement is rooted in fulfilling these needs allows organizations to create a more effective workplace culture.
Leadership styles that prioritize the well-being of employees can foster better team dynamics and promote a positive atmosphere conducive to motivation.
To implement Maslow’s theory effectively, organizations can utilize various motivation strategies, including:
- Performance incentives that reward achievements and recognize contributions.
- Training programs designed to develop skills and enhance career advancement opportunities.
- Feedback mechanisms that ensure open communication and provide constructive insights for improvement.
- Conflict resolution strategies to maintain a harmonious work environment.
- Team-building activities that strengthen relationships and collaboration among employees.
Final Thoughts
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs offers a powerful framework for understanding the complexities of human motivation and development. By recognizing and addressing the different levels of needs—from basic physiological requirements to the pursuit of self-actualization—individuals and organizations can create environments that foster personal growth, fulfillment, and productivity. Whether applied in personal development or within workplace settings, this model serves as a guide for achieving a balanced and motivated life. By aligning motivations with meaningful goals and continuously striving for higher levels of fulfillment, individuals can unlock their true potential and contribute positively to their communities and organizations.




