Multitasking does not enhance productivity; in fact, it often results in decreased performance and increased error rates. The brain struggles with task switching, leading to cognitive overload and diminished focus. This fragmentation of attention impedes effective time management and compromises the quality of work. While some view multitasking as a valuable skill, it generally leads to a false sense of accomplishment, undermining overall efficiency. Instead, adopting single-tasking practices can significantly improve focus and output quality. To understand the underlying reasons and explore practical approaches for optimizing productivity, further insights await your attention.
Key Takeaways
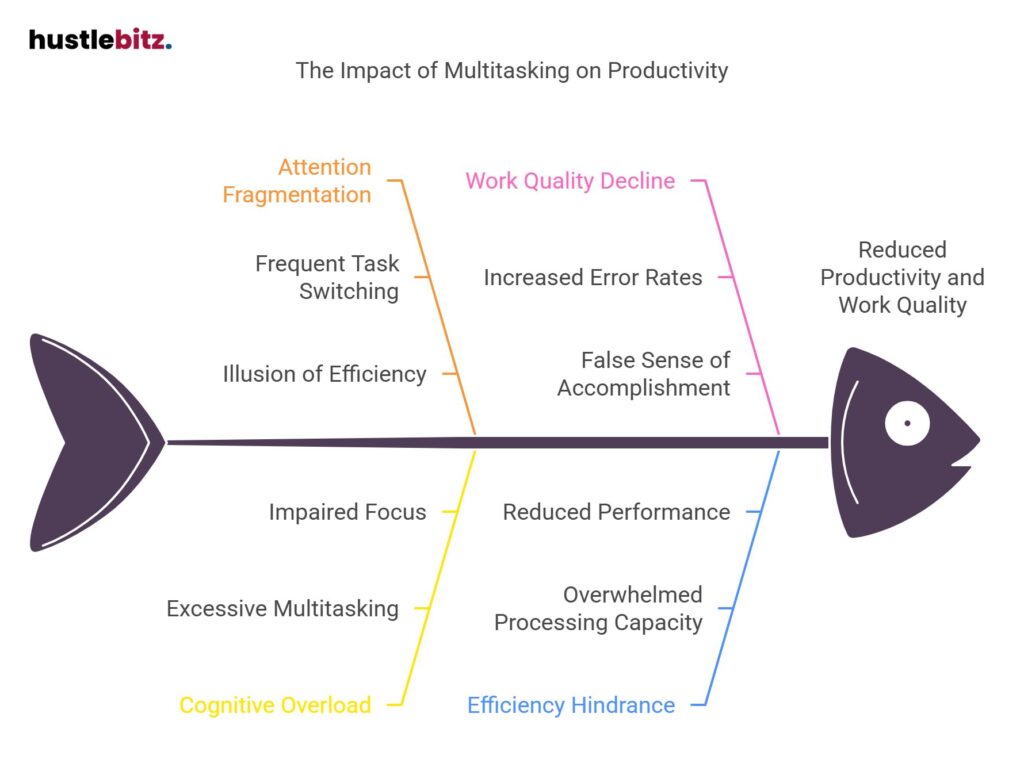
- Multitasking often leads to attention fragmentation, reducing overall productivity rather than enhancing it.
- Frequent task switching results in cognitive overload, impairing focus and increasing error rates.
- Single-tasking promotes sustained attention, leading to higher quality work and improved performance.
- Cognitive load management is critical; excessive multitasking can overwhelm processing capacity and hinder efficiency.
- The illusion of efficiency from multitasking creates a false sense of accomplishment, ultimately reducing work quality.
Understanding Multitasking

What defines multitasking, and how does it impact our cognitive processes and productivity in a fast-paced work environment?
Multitasking refers to the ability to manage multiple tasks simultaneously or switch between them efficiently. This capability relies heavily on cognitive flexibility, the brain’s ability to adapt and respond to changing demands. In today’s digital landscape, where distractions abound, maintaining an optimal attention span becomes crucial to effective multitasking.
The benefits of multitasking can manifest in improved time management and enhanced learning outcomes when tasks are adequately aligned. For instance, individuals who efficiently engage in task switching may experience heightened brain efficiency, allowing them to process information more rapidly.
However, excessive multitasking can lead to diminished focus and increased stress levels, as the brain struggles to juggle competing demands.
Workplace dynamics have evolved to embrace multitasking, often driven by the need for rapid responses and adaptability. Yet, the presence of digital distractions—such as notifications and emails—can impede performance, making it essential to strike a balance.
While multitasking can enhance productivity under certain conditions, it is vital to recognize its limitations. Overcommitting to simultaneous tasks may hinder overall effectiveness, leading to suboptimal outcomes.
The Science Behind Multitasking
Research indicates that multitasking involves complex cognitive processes that can significantly affect both performance and efficiency. Neuroscience insights reveal that when individuals engage in multitasking, the brain experiences attention shifts that can disrupt information processing. This phenomenon is often referred to as task switching, where the brain rapidly alternates between tasks rather than performing them simultaneously.
The impact of multitasking on brain efficiency is multifaceted. While cognitive flexibility allows individuals to manage multiple tasks, frequent task switching can lead to mental overload and diminish overall performance metrics. This is primarily due to dual task interference, where the simultaneous demands of multiple activities hinder the brain’s ability to function optimally.
| Aspect | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
| Cognitive Flexibility | Enhances adaptability | Can lead to decreased focus |
| Information Processing | Promotes diverse skill use | Increases likelihood of errors |
| Psychological Effects | May reduce monotony | Heightens stress and fatigue |
The psychological effects of multitasking are equally significant. While some may feel a temporary boost in productivity, the long-term consequences often include decreased efficiency and increased stress levels. Ultimately, understanding the science behind multitasking is crucial for optimizing performance and mitigating the adverse effects associated with mental overload.
Myths About Multitasking
Despite the complexities of cognitive processes involved in multitasking, several pervasive myths continue to shape perceptions about its effectiveness and benefits.
One prominent myth is that multitasking inherently boosts productivity. This misconception often leads individuals to believe they can accomplish more in less time; however, this is a classic case of efficiency illusions. In reality, multitasking frequently results in attention fragmentation, which can detract from overall productivity.
Another false assumption is that the brain can seamlessly switch between tasks without any negative repercussions. This overlooks the significant task switching pitfalls, where cognitive overload can occur, leading to a performance decline. Engaging in multiple activities at once can overwhelm our brain limitations, which are not equipped to handle simultaneous high-demand tasks effectively.
Moreover, the belief that multitasking is a skill that can be mastered contributes to productivity misconceptions. In truth, this practice often results in focus impairment, where the quality of work suffers as attention is diluted across competing tasks. Myth debunking reveals that rather than achieving more, individuals may find themselves caught in a cycle of reduced efficiency and increased errors.
Understanding these myths is crucial for fostering a more realistic perspective on productivity. By recognizing the detrimental impact of multitasking, individuals can make informed decisions about how to approach their work, ultimately promoting a more effective and focused workflow.
Cognitive Load and Performance

Cognitive load significantly influences performance, as the brain’s capacity to process information can become overwhelmed when faced with multiple simultaneous tasks. When individuals engage in task switching, they often experience a decrease in cognitive efficiency due to the limited mental bandwidth available for each task. This can lead to information overload, where the amount of information exceeds the brain’s ability to manage it effectively.
Attention allocation becomes critical in this context. When individuals attempt to juggle multiple responsibilities, they may struggle to focus on any single task, ultimately impairing memory retention and the ability to apply focus strategies. As distractions proliferate, distraction management becomes essential to maintaining productivity levels and ensuring that performance metrics remain favorable.
Cognitive flexibility is another important aspect, as it allows individuals to adapt their thinking and switch between tasks efficiently. However, excessive multitasking can hinder this flexibility, leading to diminished performance outcomes. As a result, the balance between task demands and cognitive load is vital for optimal performance.
To mitigate the negative effects of cognitive overload, individuals can employ focus strategies that prioritize essential tasks and reduce distractions. This approach not only enhances cognitive efficiency but also contributes to improved memory retention and overall performance. By recognizing the limits of cognitive capacity and implementing effective management techniques, individuals can navigate the complexities of multitasking while maintaining high productivity levels.
Impact on Work Quality

The interplay between cognitive load and multitasking significantly affects the quality of work produced, as individuals often sacrifice attention to detail and thoroughness when managing multiple tasks simultaneously.
This decline in work quality can manifest in elevated error rates, which ultimately compromise project outcomes. When individuals spread their attention across several tasks, their attention span diminishes, leading to mental fatigue that hampers both decision making and creativity levels.
Moreover, multitasking can drastically impact task efficiency. While one might assume that tackling multiple assignments at once will lead to better time management, the opposite is frequently true.
The fragmented nature of multitasking can result in longer completion times due to the constant need to refocus. This inefficiency may also diminish collaboration effectiveness, as team members may struggle to engage meaningfully when their cognitive resources are divided.
In essence, while multitasking may appear to be a solution for increasing productivity, the reality often points to a decline in work quality, undermining the very objectives it aims to achieve.
The ability to produce high-quality work hinges on sustained focus and the capacity to engage deeply with individual tasks. Therefore, organizations must weigh the potential benefits of multitasking against its adverse effects on work quality, ultimately considering the long-term implications on project outcomes and overall performance.
Multitasking Vs. Single-Tasking

Many individuals often find themselves weighing the merits of multitasking against the benefits of single-tasking in their pursuit of enhanced productivity. The prevalent belief that multitasking can maximize efficiency often veils the underlying productivity myths associated with task switching.
While some argue that juggling multiple tasks enhances cognitive flexibility, research indicates that frequent task switching can diminish attention span and lead to increased errors.
Single-tasking, conversely, emphasizes focused attention on one activity at a time. This approach allows for deeper engagement and more effective use of focus techniques, ultimately leading to more consistent performance metrics.
By allocating time effectively through structured workflow management, individuals can minimize digital distractions and enhance their overall productivity.
Efficiency strategies that prioritize single-tasking often involve breaking down larger projects into manageable segments. This method not only improves concentration but also facilitates better time allocation, ensuring that each task receives the attention it requires.
Furthermore, single-tasking can lead to a more profound sense of accomplishment, as completing tasks sequentially often results in higher quality outcomes.
Overall Effects of Multitasking

Engaging in multitasking often leads to diminished productivity and increased error rates, as the brain struggles to effectively manage multiple streams of information simultaneously. While some advocate for multitasking benefits such as enhanced cognitive flexibility and improved task switching efficiency, research suggests that these advantages are often overstated.
In reality, the demands of attention distribution across various tasks can hinder effective time management, ultimately reducing overall performance.
The influence of technology further complicates workplace dynamics. While tools designed for multitasking can facilitate quicker responses, they may also elevate stress levels and disrupt focused engagement with essential tasks. This constant switching can lead to cognitive overload, negatively impacting learning retention and personal productivity.
Furthermore, multitasking can create a false sense of accomplishment; individuals may feel busy but produce lower-quality work. In environments that require critical thinking or creativity, the adverse effects of multitasking become even more pronounced.
Workers often find that their ability to concentrate diminishes, leading to mistakes that detract from overall efficiency.
Final Thoughts
Multitasking may seem like an efficient way to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, but its drawbacks often outweigh the perceived benefits. The reality is that multitasking can lead to cognitive overload, reduced focus, and a decline in work quality. The brain’s capacity to switch between tasks is limited, and this constant shifting can impair productivity rather than enhance it. Instead, adopting single-tasking practices allows for deeper concentration, better time management, and higher-quality outcomes. By focusing on one task at a time, individuals can achieve more meaningful and lasting results. Understanding the limitations of multitasking is essential for anyone seeking to optimize their productivity and maintain a higher standard of work.




