Overcoming Imposter Syndrome involves recognizing and celebrating your achievements to build resilience and self-confidence. This psychological phenomenon often occurs among high achievers who underestimate their abilities and fear being exposed as frauds. Symptoms include persistent self-doubt, achievement denial, and perfectionism. Acknowledging personal accomplishments through journaling and self-reflection can foster a positive mindset. Techniques such as self-affirmation, positive self-talk, and goal-setting reinforce one’s strengths and potential. Embracing challenges as opportunities for growth promotes continuous improvement. To understand more about combating self-doubt and embracing your true potential, consider further exploring these approaches.
Key Takeaways
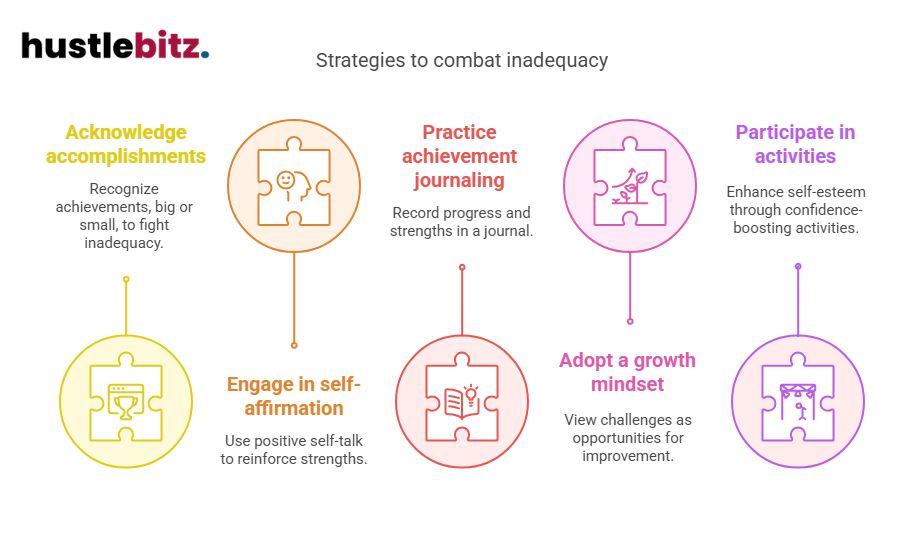
- Acknowledge and celebrate both big and small accomplishments to combat feelings of inadequacy.
- Engage in self-affirmation and positive self-talk to reinforce personal strengths and counteract self-doubt.
- Practice achievement journaling to create a tangible record of progress and strengths.
- Adopt a growth mindset by viewing challenges as opportunities for continuous improvement and personal growth.
- Participate in confidence-boosting activities like public speaking and leadership roles to enhance self-esteem.
Understanding Imposter Syndrome

Imposter Syndrome is a psychological phenomenon where individuals doubt their accomplishments and have a persistent fear of being exposed as a fraud. This imposter phenomenon is often experienced by high-achieving individuals who, despite evident success, feel unworthy of their achievements. The self-doubt dynamics at play can be particularly detrimental to those who are dedicated to serving others, as it undermines their confidence and efficacy.
Understanding the confidence paradox is crucial in addressing Imposter Syndrome. The paradox lies in the fact that those who are most competent often underestimate their abilities, while those with lesser competence might overestimate theirs. This discrepancy can lead to a skewed perception of one’s own capabilities, making achievement recognition a challenging endeavor.
Recognizing and celebrating one’s accomplishments is essential for maintaining a balanced perspective and fostering psychological resilience.
Psychological resilience is the ability to adapt and thrive despite adversity and self-doubt. For those experiencing the imposter phenomenon, building resilience involves acknowledging the internal and external factors contributing to their self-doubt dynamics. This can include societal pressures, personal upbringing, and professional environments that may inadvertently reinforce feelings of inadequacy.
Enhancing resilience requires a conscious effort to shift focus from perceived shortcomings to tangible successes and strengths.
Common Signs and Symptoms

How can one identify the presence of Imposter Syndrome in themselves or others? Recognizing Imposter Syndrome is crucial to addressing it effectively. One of the most telling signs is persistent self-doubt patterns, where individuals continuously question their own abilities and skills, regardless of evidence to the contrary. This self-doubt often leads to achievement denial, where successes are attributed to external factors like luck or timing rather than one’s own competence.
Another common symptom is an overwhelming fear of failure. Individuals with Imposter Syndrome are often paralyzed by the thought of making mistakes, which can inhibit their willingness to take on new challenges or responsibilities. This fear is frequently compounded by a comparison culture, where individuals measure their own success against the achievements of their peers, often feeling inadequate as a result.
Perfectionism traits also play a significant role. Those affected by Imposter Syndrome often set excessively high standards for themselves and are never satisfied with their performance, no matter how well they do. This relentless pursuit of perfection can lead to burnout and decreased job satisfaction.
Moreover, individuals suffering from Imposter Syndrome may display a tendency to overwork and overprepare. They may believe that they need to work harder than everyone else to prove their worth, leading to an unsustainable work-life balance.
Additionally, people with Imposter Syndrome often avoid seeking help or mentorship, fearing that doing so will expose their perceived inadequacies.
The Psychological Impact

Recognizing the signs and symptoms of Imposter Syndrome is just the beginning; understanding its psychological impact necessitates a closer examination. The pervasive cognitive distortions associated with Imposter Syndrome, such as the belief that one’s success is due to luck rather than skill, can significantly undermine emotional resilience.
This mental framework often leads individuals to engage in harmful social comparison, wherein they perceive others as more competent or deserving, thereby diminishing their own achievements and worth. These cognitive distortions not only affect professional and academic performance but also erode self-esteem and self-worth.
Individuals grappling with Imposter Syndrome frequently dismiss their accomplishments, attributing them to external factors rather than personal merit. This persistent self-doubt fosters a toxic personal narrative, perpetuating a cycle of inadequacy and anxiety. The psychological toll can be profound, manifesting as chronic stress, burnout, and even depression.
To counter these detrimental effects, adopting self-acceptance strategies becomes crucial. Encouraging individuals to reframe their personal narratives to acknowledge their true capabilities can foster a healthier self-perception.
For instance, replacing self-criticism with self-compassion can mitigate the adverse impacts of social comparison. By recognizing and celebrating their achievements, individuals can build emotional resilience, empowering them to navigate challenges with greater confidence.
Root Causes and Triggers

Understanding the root causes and triggers of Imposter Syndrome is essential for developing effective coping strategies. This phenomenon often stems from a complex interplay of childhood experiences, societal expectations, and personal tendencies that can hinder one’s self-esteem and sense of accomplishment.
Childhood experiences play a significant role in shaping our self-perception. Individuals who were subjected to high parental expectations or who faced criticism and neglect might internalize feelings of inadequacy. These early impressions can persist into adulthood, manifesting as Imposter Syndrome when achievements are met with self-doubt rather than self-assurance.
Societal expectations further exacerbate these feelings. In a culture that prizes success and high performance, the pressure to meet or exceed standards can be overwhelming. This is particularly true in professional environments where achieving excellence is often equated with personal worth. The drive to fulfill these societal norms can leave individuals constantly questioning their competencies and fearing that their shortcomings will be exposed.
Perfectionism tendencies also contribute significantly to Imposter Syndrome. Perfectionists set unrealistically high standards for themselves and are often their harshest critics. This relentless pursuit of flawlessness can lead to a paralyzing fear of failure, making it difficult for them to acknowledge their accomplishments as legitimate.
Recognizing Your Achievements

Addressing the origins and triggers of Imposter Syndrome lays a solid foundation for tackling it head-on. Once these are identified, recognizing and embracing your achievements becomes a crucial next step. By acknowledging your accomplishments, you can combat feelings of inadequacy and begin to see your true value.
Achievement journaling is a practical tool in this endeavor. By regularly documenting your successes, you create a tangible record of your progress and strengths. This practice not only highlights your achievements but also serves as a reminder during moments of self-doubt.
Self reflection practices further enhance your ability to recognize your achievements. Setting aside time to introspect allows you to understand how you’ve grown, what you’ve accomplished, and the impact you’ve made. This reflective process helps you internalize your successes and see them as a testament to your capabilities.
Incorporating gratitude exercises into your routine can also be beneficial. Expressing gratitude for your achievements, no matter how small, cultivates a positive mindset and reinforces the importance of acknowledging your efforts.
Peer recognition plays a significant role as well. Seeking feedback and validation from trusted colleagues can provide an external perspective on your accomplishments, reinforcing your sense of worth and capability.
Lastly, celebrating milestones is vital. Recognizing and celebrating your achievements, both big and small, helps to solidify your sense of accomplishment. Whether it’s through a small reward or a simple acknowledgment, celebrating these moments reinforces the value of your hard work.
- Achievement journaling
- Self reflection practices
- Gratitude exercises
- Peer recognition
- Celebrating milestones
Building Self-Confidence
Building self-confidence is a multifaceted process that requires deliberate effort and consistent practice. For individuals committed to serving others, enhancing one’s self-confidence is not merely a personal endeavor but a vital component in effectively supporting and inspiring those around them.
One effective approach is to engage in self-affirmation strategies. These involve regularly acknowledging personal strengths and accomplishments, which can counteract negative self-perceptions. For example, writing daily affirmations or reflecting on past successes can reinforce a positive self-image.
Confidence boosting activities are another essential element. These activities can range from public speaking engagements to volunteering in leadership roles. Such experiences not only build competence but also provide tangible evidence of one’s capabilities, fostering greater self-assurance.
Incorporating positive self-talk into daily routines is also crucial. This involves consciously replacing self-doubt with encouraging and constructive thoughts. Instead of focusing on potential failures, one can remind themselves of their skills and past achievements, creating a mental environment conducive to confidence.
Visualization techniques can further enhance self-confidence. By mentally rehearsing successful outcomes and envisioning oneself achieving goals, individuals can reduce anxiety and increase their belief in their own abilities. This practice helps create a mental blueprint for success, making the path forward feel more attainable.
Lastly, goal setting practices are instrumental in building self-confidence. Setting and achieving small, incremental goals can provide a sense of accomplishment and momentum. This structured approach not only clarifies one’s direction but also demonstrates personal growth and capability over time.
Cultivating a Growth Mindset

Enhancing self-confidence lays a foundation for further personal development, which can be significantly bolstered by cultivating a growth mindset. This mindset emphasizes the belief that intelligence, abilities, and talents can be developed through dedication and hard work. For individuals keen on serving others, adopting such an outlook can be transformative, enabling them to overcome imposter syndrome and unlock their full potential.
Key to this transformation are growth strategies that focus on continuous improvement and learning. These strategies involve mindset shifts where challenges are seen as opportunities rather than obstacles. This perspective encourages resilience building, allowing individuals to recover from setbacks stronger and more determined.
Self reflection exercises play a crucial role in this process, helping individuals to recognize their progress and areas for improvement. By regularly engaging in these exercises, one can maintain a balanced view of their achievements and shortcomings, fostering a healthier self-perception.
Furthermore, lifelong learning is a cornerstone of a growth mindset. Embracing the journey of constant education and skill enhancement equips individuals to better serve others, as they are always evolving and adapting to new challenges and opportunities.
To summarize, consider the following actionable steps to cultivate a growth mindset:
- Adopt growth strategies: Focus on continuous improvement and learning.
- Mindset shifts: View challenges as opportunities for growth.
- Resilience building: Develop the ability to recover from setbacks.
- Self reflection exercises: Regularly assess your progress and areas for improvement.
- Lifelong learning: Commit to ongoing education and skill development.
Embrace Your Potential
Regularly embracing your potential is crucial for overcoming imposter syndrome and achieving personal and professional growth. This process begins with a self discovery journey, where you identify your unique strengths, talents, and areas of expertise. Understanding these elements allows you to set realistic and meaningful goals that align with your core values and aspirations.
Incorporating positive affirmations into your daily routine can significantly bolster your self-confidence. By consistently reminding yourself of your capabilities and past achievements, you counteract the negative self-talk that fuels imposter syndrome. This practice not only nurtures a healthier self-image but also encourages you to take on new challenges with a more optimistic outlook.
Mindfulness practices play a pivotal role in embracing your potential. Techniques such as meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and mindful reflection help you stay present and focused. This heightened awareness enables you to recognize moments of self-doubt and address them constructively. By being mindful, you create a mental space conducive to positive thinking and resilience.
Goal setting is another essential component in this journey. Establishing clear, attainable objectives provides a roadmap for your personal growth. Breaking down larger goals into smaller, manageable tasks ensures steady progress and reduces the overwhelm often associated with ambitious pursuits.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting these goals keeps you aligned with your evolving aspirations and continuously moving forward.
Ultimately, embracing your potential is about recognizing and harnessing your inherent abilities to serve others effectively. By embarking on a self discovery journey, engaging in positive affirmations, practicing mindfulness, and setting clear goals, you create a solid foundation for lasting personal and professional success.
Final Thoughts
Overcoming Imposter Syndrome requires a conscious effort to recognize and embrace your achievements, while also understanding the root causes of self-doubt. By practicing self-affirmation, engaging in positive self-talk, and adopting a growth mindset, you can gradually build confidence and resilience. This journey involves recognizing your strengths, setting realistic goals, and viewing challenges as opportunities for growth. With consistent self-reflection and mindfulness, you can move beyond the fear of inadequacy, fully embrace your potential, and continue to grow both personally and professionally.




