Cognitive Behavioral Motivation (CBM) combines cognitive and behavioral principles to foster understanding and enhancement of motivation. This approach highlights how thoughts influence emotions and actions, thereby shaping mental health and behavior management strategies. Key components include cognitive restructuring, self-efficacy, and positive reinforcement, which help individuals overcome negative thought patterns and engage more effectively with their goals. CBM is applied across educational, clinical, and workplace settings to improve motivation and resilience. By recognizing and addressing maladaptive beliefs, individuals can cultivate a constructive mindset, paving the way for sustained personal and professional growth. Further insights into this transformative approach await exploration.
Key Takeaways
- Cognitive Behavioral Motivation (CBM) integrates cognitive processes and behavior to enhance personal growth and resilience.
- Cognitive restructuring helps challenge negative thought patterns, fostering increased motivation and goal achievement.
- Positive reinforcement and self-monitoring are vital techniques that bolster sustained motivation and encourage desired behaviors.
- CBM effectively addresses mental health issues, promoting healthier thinking patterns and improved emotional well-being.
- The adaptable nature of CBM makes it suitable for diverse populations facing various psychological challenges.
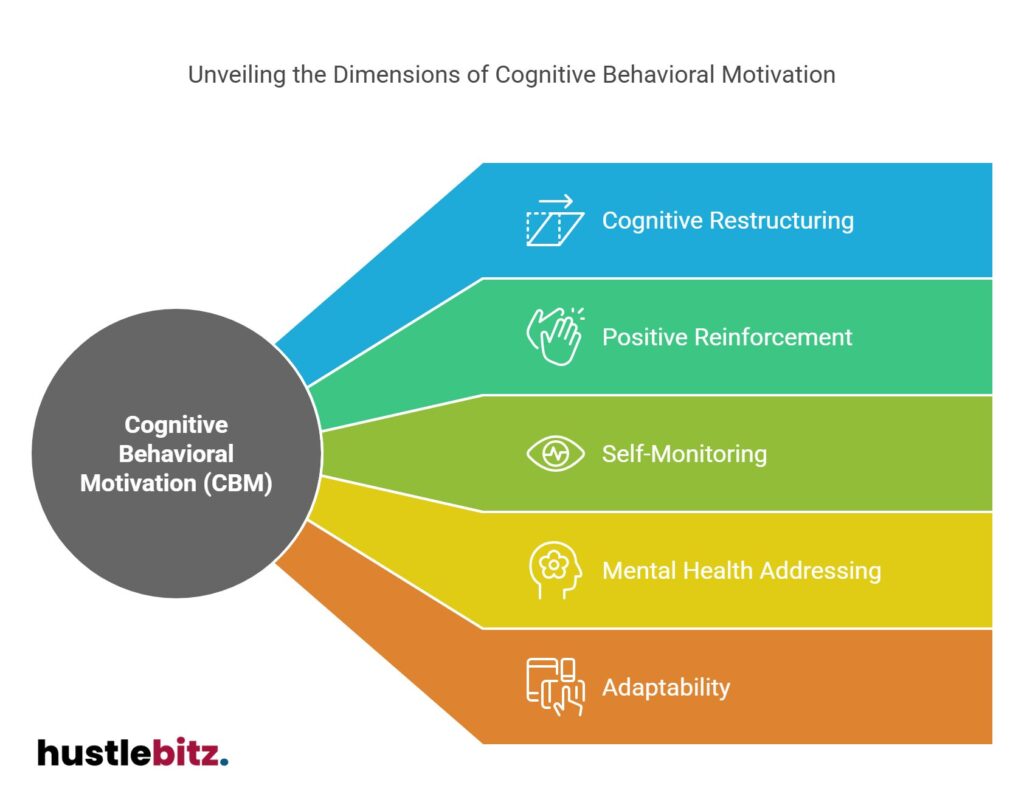
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Motivation

What drives individuals to change their behaviors and thoughts? Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Motivation involves examining the interplay between cognitive processes and behavioral outcomes in fostering personal growth and psychological resilience. This approach underscores the belief that our thoughts significantly influence our emotions and actions, thereby shaping our overall mental health.
Cognitive behavioral motivation is predicated on the idea that individuals can harness their cognitive processes to effectuate meaningful change in their lives. By identifying maladaptive thought patterns, individuals can engage in behavior management strategies that promote more adaptive responses. This process is not merely reactive; rather, it is proactive and constructive, encouraging individuals to reframe their perceptions and beliefs to enhance motivation.
The role of motivation within this framework is pivotal. It serves as the catalyst for change, driving individuals to adopt healthier behaviors and discard those that may be detrimental to their well-being. By fostering an understanding of how cognitive processes influence motivation, individuals can better equip themselves to navigate challenges and setbacks.
Ultimately, the synergy between cognitive behavioral theories and motivational strategies empowers individuals to cultivate resilience. Through targeted interventions that address both cognition and behavior, individuals can achieve lasting transformation, improving not only their mental health but also their overall quality of life.
Theoretical Foundations of CBM

How do theoretical frameworks underpinning Cognitive Behavioral Motivation (CBM) inform our understanding of behavior change and emotional regulation?
At the intersection of cognitive theories and behavioral practices, CBM offers a structured approach to understanding how thoughts influence emotions and actions. By integrating principles from cognitive behavioral approaches, it illuminates the pathways through which motivation in learning can be enhanced.
The theoretical foundations of CBM can be summarized through three key concepts:
- Cognitive Restructuring: This involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns that inhibit motivation. By reframing these thoughts, individuals can foster a more positive outlook that promotes emotional regulation.
- Self-Efficacy: Central to motivation, self-efficacy refers to an individual’s belief in their ability to succeed in specific situations. This belief can significantly impact one’s willingness to engage in challenging tasks and persist in the face of obstacles.
- Positive Psychology: This perspective emphasizes the importance of strengths and well-being in fostering motivation. By focusing on positive experiences and outcomes, individuals can cultivate resilience and a greater capacity for emotional regulation.
Together, these foundations create a comprehensive framework that guides individuals in understanding their behaviors and emotional responses.
Key Principles of CBM

Emphasizing the interplay between cognition and behavior, the key principles of Cognitive Behavioral Motivation (CBM) provide a framework for understanding and enhancing individual motivation through targeted cognitive and behavioral strategies.
At the heart of CBM is the concept of cognitive motivation, which posits that an individual’s thoughts significantly influence their willingness to engage in specific behaviors. This principle suggests that by modifying maladaptive thought patterns, individuals can improve their motivation levels.
Another critical component of CBM is the emphasis on emotion regulation. Effective emotion regulation strategies can help individuals manage their emotional responses, leading to more adaptive behaviors and improved motivation. For instance, by cultivating positive emotional states, individuals can enhance their focus and persistence toward achieving their goals.
Furthermore, CBM recognizes the impact of behavioral reinforcement on motivation. Positive reinforcement, such as rewards for academic achievements, can significantly enhance motivation and lead to improved academic outcomes. Conversely, a lack of reinforcement or negative feedback may contribute to decreased motivation and reinforce maladaptive behavior.
Lastly, the integration of cognitive-behavioral techniques allows for the identification and restructuring of unhelpful beliefs that hinder motivation. By addressing these cognitive distortions, individuals can foster a more constructive mindset, thereby promoting sustained motivation and better performance.
The Role of Thoughts in Motivation
Thoughts play a crucial role in shaping motivation, as they directly influence an individual’s perception of challenges, goals, and their ability to succeed. Cognitive processes determine how we interpret our experiences, which in turn affects our motivation levels. Understanding the interplay between thoughts and motivation can lead to more effective behavior patterns and enhanced goal achievement.
Several key aspects illustrate how thoughts contribute to motivation:
- Cognitive Appraisal: The way individuals appraise a situation can either bolster or undermine their motivation. Positive thoughts can foster resilience, while negative thoughts may create barriers.
- Goal Setting: Cognitive clarity regarding one’s goals is essential for sustained motivation. When thoughts are aligned with achievable targets, commitment increases, and individuals are more likely to engage in behaviors that lead to success.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): This therapeutic approach emphasizes accepting thoughts rather than avoiding them. By recognizing and understanding cognitive processes, individuals can develop a more reliable and valid framework for addressing challenges, thus enhancing motivation.
Behavioral Techniques in CBM

Behavioral techniques in Cognitive Behavioral Motivation (CBM) are essential tools designed to modify actions and reinforce positive behaviors, ultimately enhancing motivation and goal attainment. These techniques focus on the interplay between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, employing a cognitive-behavioral framework to facilitate change. By addressing maladaptive behaviors through structured interventions, practitioners can help individuals identify and alter patterns that hinder motivation.
One significant aspect of behavioral techniques in CBM involves setting specific, measurable goals. This process not only provides clear targets for individuals but also fosters a sense of accomplishment as they progress. Additionally, positive reinforcement plays a crucial role; rewarding desired behaviors encourages their repetition, thereby solidifying motivational growth.
Another effective intervention is the use of self-monitoring, where individuals track their behaviors and thoughts. This heightened awareness allows for the identification of triggers and patterns that may contribute to demotivation or counterproductive actions. Cognitive restructuring, a cognitive-behavioral strategy, can also be integrated into behavioral techniques to challenge negative thought patterns that impede motivation.
Moreover, developing coping strategies is vital within CBM. These strategies equip individuals with tools to manage setbacks and obstacles, thus maintaining motivation over time.
Practical Applications of CBM

Cognitive Behavioral Motivation (CBM) finds practical applications across various domains, including education, clinical settings, and workplace environments, where it enhances individual performance and well-being.
By utilizing the cognitive behavioral approach, practitioners can effectively address motivation-related challenges through structured strategies that promote positive change.
The following are three key practical applications of CBM:
- Education: In educational settings, CBM techniques can help students overcome procrastination and improve their study habits. By identifying and restructuring negative thought patterns, educators can foster a growth mindset, thus enhancing students’ intrinsic motivation and academic performance.
- Clinical Settings: In therapy, CBM is instrumental in treating anxiety and depression. Therapists employ cognitive behavioral techniques to help clients understand their thoughts and behaviors, encouraging assertiveness training to boost self-esteem and coping strategies. This approach empowers clients to take control of their mental health.
- Workplace Environments: In a corporate context, CBM can enhance employee motivation and productivity. Through tailored training programs, organizations can implement cognitive behavioral strategies that address workplace stressors and promote assertiveness among employees, leading to a more engaged and motivated workforce.
Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Motivation

Enhancing motivation through Cognitive Behavioral Motivation (CBM) offers numerous benefits that significantly impact personal growth and well-being across various settings. One of the primary advantages of CBM is its focus on fostering self-efficacy, enabling individuals to set and achieve realistic goals. This approach employs positive reinforcement techniques, which encourage sustained engagement and motivation by recognizing and rewarding progress.
Additionally, CBM provides a framework for reliable measurement of behavioral changes, allowing practitioners to assess the effectiveness of interventions systematically. Treatment studies have demonstrated that individuals who utilize CBM techniques often experience increased motivation and improved mental health outcomes. The structured nature of this psychological approach helps individuals identify cognitive distortions and develop healthier thinking patterns, further enhancing their motivation.
Moreover, the adaptability of CBM makes it applicable across diverse populations, including those dealing with anxiety, depression, and other psychological challenges. By addressing the underlying cognitive processes that influence motivation, CBM equips individuals with practical tools to navigate obstacles and maintain focus on their goals.
Overcoming Negative Thought Patterns
Overcoming negative thought patterns is essential for fostering a mindset conducive to motivation and personal growth. These patterns can hinder individuals from pursuing their goals and achieving success. By employing a cognitive-behavioral approach, one can systematically identify and challenge these detrimental thoughts, leading to improved emotional well-being and enhanced motivation.
To effectively overcome negative thought patterns, consider the following strategies:
- Cognitive Restructuring: This involves recognizing and reframing irrational beliefs. By questioning the validity of negative thoughts, individuals can replace them with more balanced and constructive alternatives.
- Behavioral Activation: Engaging in activities that bring joy or fulfillment can counteract feelings of negativity. This proactive approach can enhance motivation and create positive experiences that diminish the power of negative thoughts.
- Mindfulness Practices: Incorporating mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or deep-breathing exercises, can help individuals become aware of their thoughts without judgment. This awareness allows for a more objective perspective, making it easier to detach from negative thought patterns.
Embracing these strategies not only facilitates the process of overcoming negative thought patterns but also promotes a healthier psychological state. By utilizing a cognitive-behavioral framework, individuals can cultivate a more positive mindset, which is integral to sustaining motivation and achieving personal growth.
The journey toward overcoming negativity is not merely about eliminating harmful thoughts; it is about actively fostering a resilient and empowered self.
Final Thoughts
Cognitive Behavioral Motivation (CBM) offers a powerful framework for enhancing motivation by integrating cognitive and behavioral strategies. By addressing negative thought patterns and reinforcing positive behaviors, individuals can cultivate resilience and achieve sustained personal and professional growth. Whether applied in educational settings, clinical practice, or workplace environments, CBM provides practical tools for overcoming obstacles and fostering a constructive mindset. Embracing this approach can lead to lasting improvements in both mental health and overall well-being, making it a valuable resource for anyone seeking to enhance their motivation and achieve their goals.




